Good Feature Matching in BA-SLAM
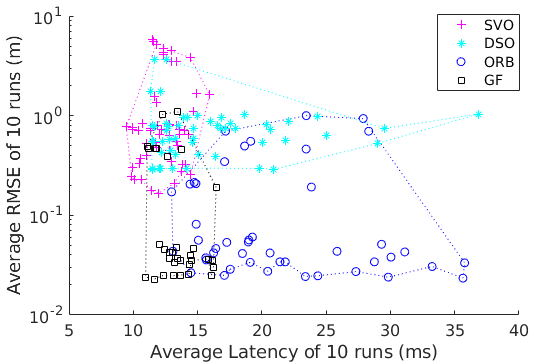
Abstract: Active map-to-frame matching using SLAM condition scoring is proposed for balancing time cost and accuracy in indirect, BA-SLAM. Exploiting the submodularity property of pose optimization condition scoring leads to an algorithm for deciding when to employ map-to-frame matching, how many points to select, and how to prioritize the data association to best benefit pose estimation outcomes. When applied to ORB-SLAM, the algorithmic modification lowers run-time costs without impacting localization performance.
Map-Hash for Fast Local-Map Queries
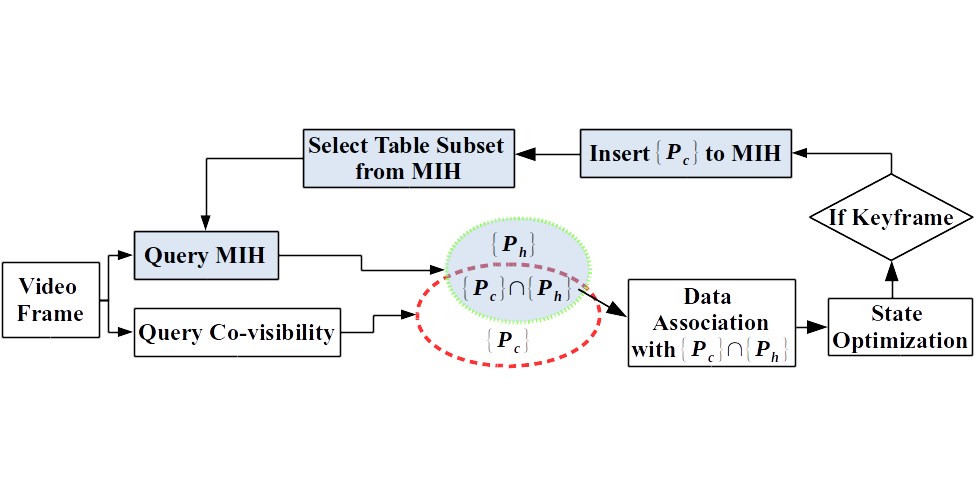
Abstract: Long-term, large-area SLAM performance is best when it is possible to match previously seen (but subsequently lost) map points when they re-enter the field-of-view and are visible once more. However, the time cost associated to matching against an ever increasing map undermines real-time performance. We combine hashing and condition scoring to arrive at a fast, bounded map-to-frame method we call Map-Hash. The value of Map-Hash is shown on a modified ORB-SLAM implementation relative to baseline ORB-SLAM.
Good Feature Selection in BA-SLAM
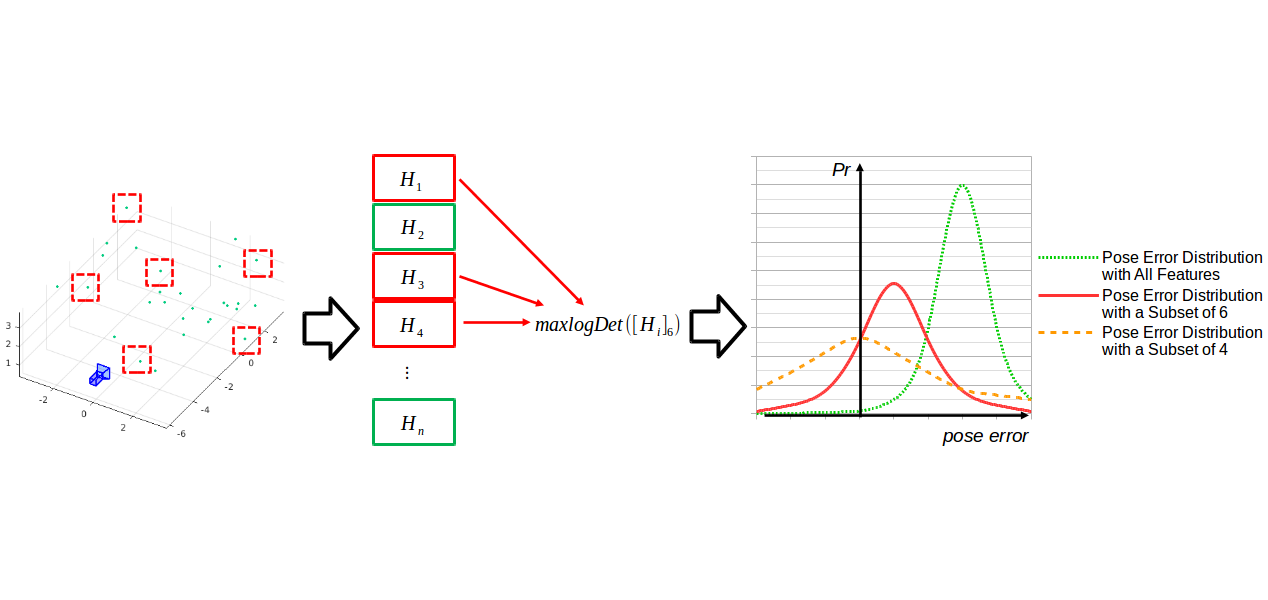
Abstract: SLAM condition scoring as a means to derive robust camera pose estimation methods for bundle-adjustment based SLAM are explored and shown to improve pose accuracy by 30% while increasing runtime by only 2%. The key idea is to perform inlier selection of tracked feature points so that the local pose optimization has strong conditioning. Combining this geometric conditioning with appearance-based match scoring leads to the stated outcomes.
Optimal Observability and Maximal Cardinality
Abstract:
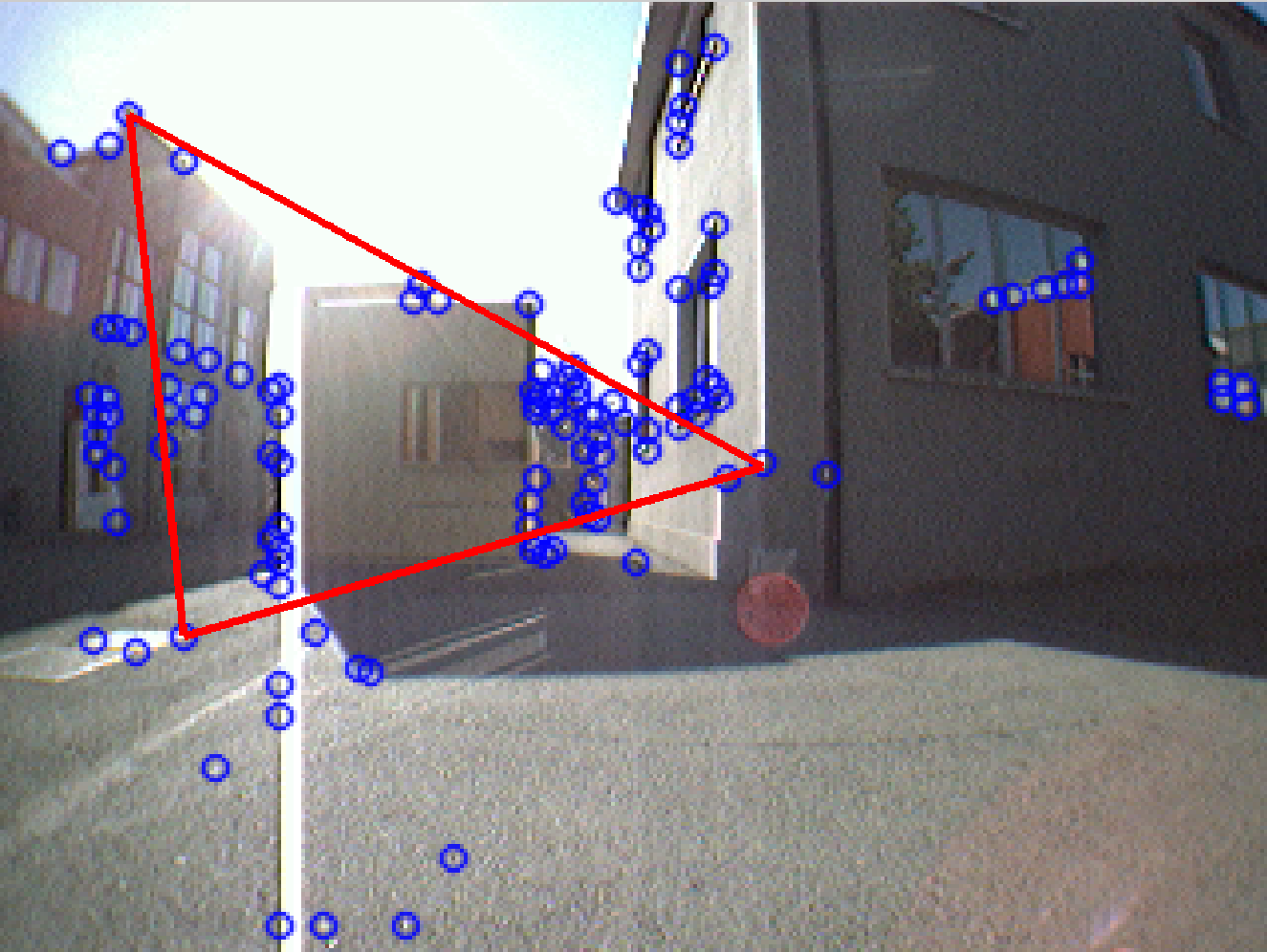
Uses the good features for SLAM concept to propose a deterministic process
for inlier estimation that matches RANSAC performance while having a more
consistent time cost relative to RANSAC.
Measurement selection and outlier rejection use feature condition scoring
and hypothesis testing. The outcomes suggest that randomized methods can be
superceded by bounded or fixed time-cost deterministic methods based on
feature point scoring.
